
501 AR120
Billing and Accounts Receivable Overview
Web Based Training
Rev 11/23/2021

This training provides participants with the skills and information necessary to use Cardinal and is not intended to
replace existing Commonwealth and/or agency policies.
This course, and the supplemental resources listed below, are located on the Cardinal website
(www.cardinalproject.virginia.gov) under Learning.
Cardinal Reports Catalogs are located on the Cardinal website under Resources:
• Instructor led and web based training course materials
• Job aids on topics across all functional areas
• Variety of simulations
• Glossary of frequently used terms
The Cardinal screenshots included in this training course show system pages and processes that some users
may not have access to due to security roles and/or how specific responsibilities relate to the overall transaction
or process being discussed.
For a list of available roles and descriptions, see the Statewide Cardinal Security Handbook on the Cardinal
website in the Security section under Resources.
1
Welcome to Cardinal Training

After completing this course, you will be able to:
2
Course Objectives
Understand the two Accounts Receivable modules: Accounts Receivable and Billing
Identify the five Accounts Receivable processes
Understand how Accounts Receivable integrates with other Cardinal functional areas and
interfaces with external entities

This lesson covers the following topics:
• Billing and Accounts Receivable Overview
• Key Concepts
4
Lesson 1: Introduction
1
Introduction to Accounts Receivable

The Accounts Receivable functional area of Cardinal
is composed of two modules:
Accounts Receivable
The Accounts Receivable module manages the
processing of payments that are due to the agency.
Billing
The Billing module includes the processes for creating
invoices, reviewing and validating invoices, and
managing billing and distribution cycles.
5
Billing and Accounts Receivable Overview

Key concepts in Billing and Accounts Receivable include:
• Billing and Accounts Receivable are two separate modules within the Accounts Receivable functional
area.
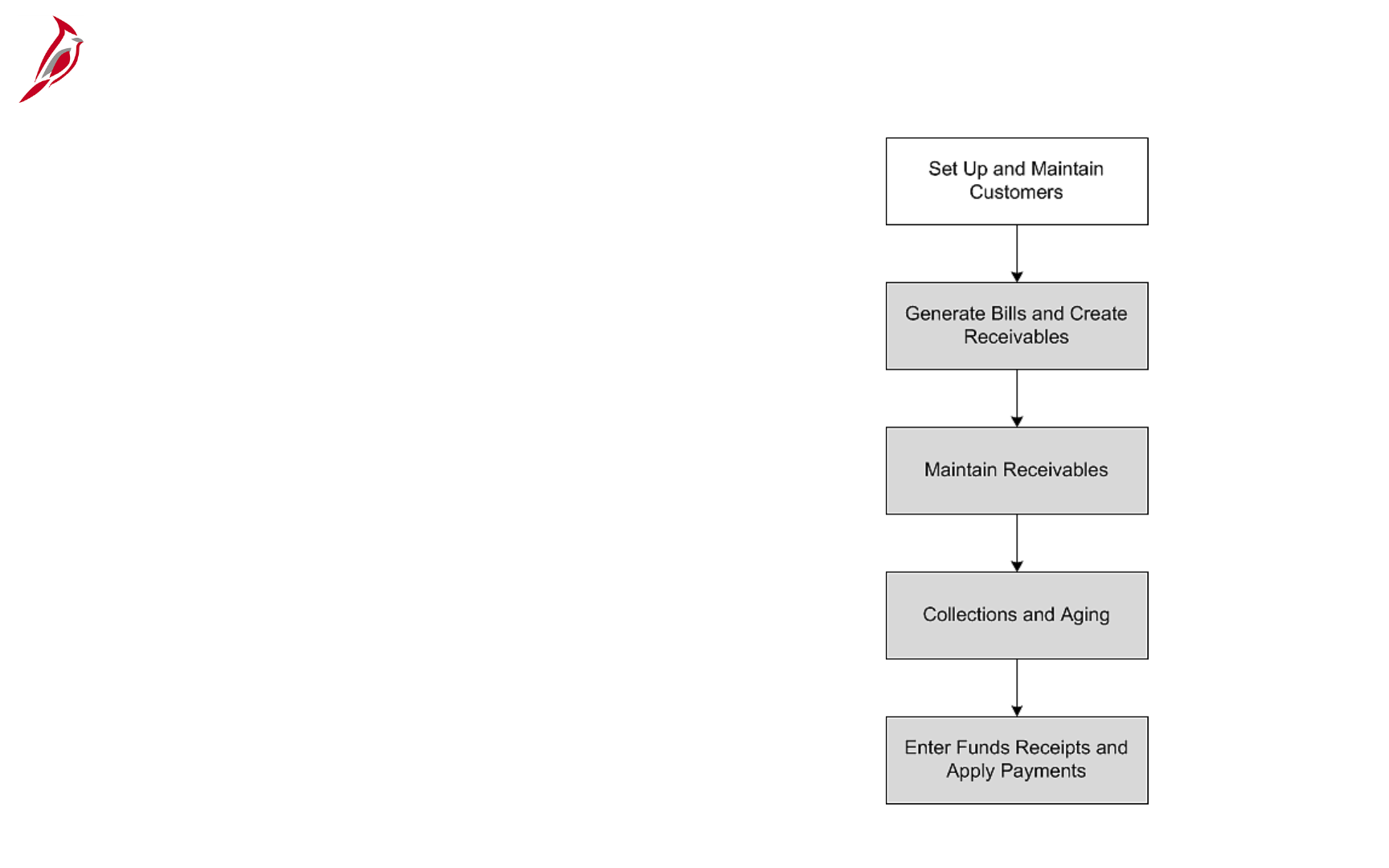
• These two modules support five key processes in the Accounts Receivable functional area:
• Set up and Maintain Customers
• Generate Bills and Create Receivables
• Maintain Receivables
• Collections and Aging
• Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments
• Four types of billing invoices can be created in Cardinal:
• Standard
• Recurring
• Installment
• Consolidated
6
Key Concepts

7
Key Concepts (continued)
• Payments received may be:
• Applied against accounts receivable items (when there is no related accounts receivable item).
• Entered as direct journals (when there is no related accounts receivable item)
• The Accounts Receivable functional area integrates with Project Costing and General Ledger, and
interfaces with the Department of Taxation, the Department of Treasury, and the Federal Highway
Administration.

In this lesson, you learned:
• Accounts Receivable functional area is composed of two modules: the Accounts Receivable module and
the Billing module
• There are five processes contained within the Billing and Accounts Receivable modules:
• Set up and Maintain Customers
• Generate Bills and Create Receivables
• Maintain Receivables
• Collections and Aging
• Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments
Lesson 1: Summary
1
Introduction to Accounts Receivable
8

This lesson covers the following topics:
• Accounts Receivable Functional Area
• Set up and Maintain Customers Process
• Billing Module
• Generate Bills and Create Receivables Process
• Accounts Receivable Module
• Maintain Receivables Process
9
Lesson 2: Introduction
2
Accounts Receivable Processes

• Collections and Aging Process
• Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments Process
10
Lesson 2: Introduction (continued)
2
Accounts Receivable Processes

Key processes in the Accounts Receivable functional
area are:
• Setup and Maintain Customers - Enter and
maintain customers, billing, and miscellaneous
information.
• Generate Bills and Create Receivables - Enter
billing information, create billing invoices, and
create and post Accounts Receivable items.
• Maintain Receivables - Maintain accurate
receivable balances using refunds, write-offs,
debit / credit memos, non-sufficient funds, and
transferring receivable amounts.
• Collections and Aging - Collect payments for
receivables and identify and calculate the age of
receivable balances in order to initiate appropriate
collection procedures.
• Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments -
Create deposits and apply payments to
appropriate accounts receivable items.
11
Accounts Receivable Functional Area
The Set Up and Maintain Customers process includes
the initial setup of customers as well as ongoing
maintenance.
12
Set Up and Maintain Customers Process

The Set Up and Maintain Customers process involves:
• Receiving customer information
• Determining whether the customer already exists
• Manually entering or updating customer information billing information and contact information
Once customers are created, they are available for use in the Billing and Accounts Receivable modules.
13
Set Up and Maintain Customers Process (continued)

The Set Up and Maintain Customers process involves several key steps:
• Receive Request to Set Up a Customer - A request may come from an external source (e.g., a State
Police accident report), or it may come from another functional area (e.g., request from Project
Accounting to bill another agency for costs related to a project).
• Verify the Customer Does Not Already Exist - Check the customer master records and verify that the
customer has not already been entered.
• Enter General Information - Enter general information for a new customer or update general information
for an existing customer.
• Enter Billing Information - Select various billing options for a customer, bill types, cycles (daily, monthly,
quarterly, etc.), forms, and payment methods (credit card, check, etc.).
• Enter Customer Contact Information - Customer contact phone and address information can be
entered/updated.
• Maintain Customer Information - Update customer type/general information, update correspondence
options, and create attachments and notes. For a detailed listing of the file extensions that are allowed as
attachments in Cardinal, see the appendix section of this course.
14
Set Up and Maintain Customers Process (continued)

Access the Set Up and Maintain Customers processes on the Customers menu.
Navigate to this page using the following path: Main Menu > Customers.
Select the Customer Information link, then select General Information.
15
Set Up and Maintain Customers Process (continued)

The General Information pages store the information needed to manage customers, including names and
addresses, contact information, payments terms, and billing and shipping information.
When the customer setup is complete, Cardinal assigns a sequentially numbered Customer ID.
16
Set Up and Maintain Customers Process (continued)

The Billing module contains the Generate Bills and
Create Receivables process.
17
Generate Bills and Create Receivables

The Generate Bills and Create Receivables process includes:
• Entering bill information
• Creating, reviewing and validating invoices
• Managing billing cycles
• Creating receivables
18
Generate Bills and Create Receivables (continued)

The key steps in the Generate Bills and Create Receivables process are:
• Enter Online Bills - Create standard bills, recurring bills, installment bills, and consolidated bills.
• Create Invoices - An invoice is a bill that has been processed and is ready to go out to a customer.
Invoices are created for billable transactions interfaced from the Project Costing/Customer Contracts
modules or when bills are entered online. Invoices can be created as PDFs.
• Edit Bills - You can adjust an entire bill or a portion of a bill.
• Process Invoices - Once processed, the Invoice Register can be printed and the invoices mailed to the
customers.
• Post Receivables - The billing process generates accounts receivable which are then posted to General
Ledger.
19
Generate Bills and Create Receivables (continued)

Billing processes are accessed on the Billing menu.
Navigate to this page using the following path: Main Menu > Billing
For example, to create a standard bill select the Maintain Bills link, then select Standard Billing.
20
Generate Bills and Create Receivables (continued)

The Standard Billing page is used to create a standard (regular) online bill.
21
Generate Bills and Create Receivables (continued)

22
Accounts Receivable Module
The Accounts Receivable processes include:
• Maintain Receivables – Use the following to update
receivable balances
• Adjust receivable balances (including refunds)
• Create a write-off
• Record non-sufficient funds
• Transfer receivable amounts
• Collections and Aging - These processes allow
identifying and analyzing aged receivables in order
to initiate the appropriate collection procedures
• Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments: These
processes allow creating deposits and applying
payments to Accounts Receivable or creating direct
journal entries to send to General Ledger

The Accounts Receivable module posts entries
generated during these processes to General Ledger.
General Ledger updates Accounts Receivable with
identifying information (Journal ID, Date, etc.) so
entries can be easily traced through Cardinal.
Accounts Receivable also shares Collections and
Aging data with external 3
rd
party systems.
23
Accounts Receivable Module (continued)

The Accounts Receivable menu option gives access to the major functions in Accounts Receivable.
Navigate to this page using the following path:
Main Menu > Accounts Receivable
24
Accounts Receivable Module (continued)

The Maintain Receivables process helps end users to manage receivable balances.
Maintenance is performed using a maintenance worksheet, which is a workspace for offsetting items, write-
offs, or adjustments.
Receivables maintenance items include debit or credit memos, adjustments, on-account payments, and
matches. Maintenance worksheets can be used to refund an item with a credit balance or to create a new
refund item for a credit remaining from maintenance tasks.
25
Maintain Receivables

Navigate to the Create Worksheet page using the following path:
Main Menu > Accounts Receivable > Receivables Maintenance > Maintenance Worksheet > Create
Worksheet
26
Maintain Receivables (continued)

The aging process is a tool used to calculate the age of outstanding customer accounts receivable balances.
This process runs nightly and automatically categorizes receivables by date.
The Aging process updates summary aging information that appears on various inquiry pages.
Management and collection departments rely on aging to identify delinquent accounts and take appropriate
action.
27
Collections and Aging

There are several aging reports that show the history and category of the item. For example, you can use the
Aging Summary by Unit report can be used to see aged open balances for every customer in a business
unit.
Navigate to this page using the following path:
Main Menu > Accounts Receivable > Receivables Analysis > Aging > Aging Summary by Unit Rpt
28
Collections and Aging (continued)

Payments may or may not correspond to an open Accounts Receivable item.
• If the payment corresponds to an Accounts Receivable item, a payment worksheet is created so that the
payment is applied to the item. The worksheet is saved for further processing and posting.
• If the payment does not correspond to an Accounts Receivable item, it will be recorded as a Direct
Journal.
Identifying information for payments related to receivable items. This identifying information, such as an Item
ID or Customer ID, is entered to aid application of payments that reduce the receivable balances.
29
Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments

Deposits and payments posted to the Accounts Receivable module are posted to the invoices created in the
Billing module.
Navigate to this page using the following path:
Main Menu > Accounts Receivable > Payments > Online Payments > Regular Deposit
30
Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments (continued)

Now is your opportunity to check your understanding of the course material.
Read the question on the next slide(s), select answer(s) and click Submit to see if you chose the correct
response.
31
Lesson 2: Checkpoint

32

33

In this lesson, you learned:
• Set up and Maintain Customers
• Generate Bills and Create Receivables
• Maintain Receivables
• Collections and Aging
• Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments
Lesson 2: Summary
2
Accounts Receivable Processes
34

This lesson covers the following topics:
• Integration with General Ledger and Project Accounting
• Interfaces
35
Lesson 3: Introduction
3
Billing and Accounts Receivable Integration and Interfaces

Accounts Receivable sends accounting entries to the General Ledger.
The Project Costing/Customer Contracts module sends project billing data to the Billing module in the
Accounts Receivable functional area. The Billing module then creates the related invoices and accounting
entries.
Once the invoices are final, related billing data is available to upload to the Customer Contracts and Project
Costing modules.
Adjustments made to billing or receivables create entries that update project information in the Project
Costing module.
36
Integration with General Ledger and Project Accounting

37
Integration with General Ledger and Project Accounting
Accounts
Receivable

Accounts Receivable also interfaces with other systems outside of Cardinal, including the following:
Department of Taxation - Accounts Receivable sends and receives collection data to and from
the Department of Taxation during the Collections and Aging process. Accounts Receivable receives
payment data from the Department of Taxation in the Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments
process. These interfaces allow us to collect past-due receivables from any payments another state agency
might make to the customer.
Department of Treasury - Accounts receivable sends finalized deposit data to the Department of Treasury.
The data is uploaded to their reconciliation system daily, and is used to reconcile deposit data from Cardinal
with that of bank statements.
Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) - Cardinal Accounts Receivable also sends Project Billing Data to
FHWA on a daily basis.
38
Interfaces

Now is your opportunity to check your understanding of the course material.
Read the question on the next slide(s), select answer(s) and click Submit to see if you chose the correct
response.
39
Lesson 3: Checkpoint

40

In this lesson, you learned:
• The Accounts Receivable functional area integrates with two other functional areas in Cardinal: General
Ledger and Project Costing.
• The Accounts Receivable functional area interfaces with other major systems including Department of
Taxation, Department of Treasury, and the Federal Highway Administration.
Lesson 3: Summary
3
Billing and Accounts Receivable Integration and Interfaces
41

In this course, you learned:
• The Accounts Receivable functional area is composed of two modules: Accounts Receivable and Billing.
• The five Accounts Receivable processes are:
- Set Up and Maintain Customers
- Generate Bills and Create Receivables
- Maintain Receivables
- Collections and Aging
- Enter Funds Receipts and Apply Payments
• Accounts Receivable integrates with other Cardinal functional areas and interfaces with external entities.
42
Course Summary
AR120
Billing and Accounts Receivable Overview

Congratulations! You successfully completed the 501 AR120: Billing and Accounts Receivable Overview
course.
Click here to access the evaluation survey for this course.
Once you have completed and submitted the survey, close the survey window. To close the web based
training course, click the [X] button in the upper right corner.
43
Course Evaluation

• Key Terms
• Allowed Extensions on Attachments in Cardinal
• Flowchart Key
44
Appendix

Aging Process: Tool that calculates the age of outstanding customer accounts receivable balances.
Management and collection departments rely on aging reports to identify delinquent accounts and take
appropriate action.
There are five aging type options available in Cardinal.
• Dispute Aging
• Deduction Aging
• Collection Aging
• Doubtful Aging
• Draft Aging
Customer: An entity responsible for paying the agency.
In Cardinal there are four general customer types available
• Government (Federal, City, County, or Town)
• Business
• Individual
• State Agency
Deposits: Payments received from customers. A payment can be applied to multiple items for a single
customer or to multiple items from different customers.
Installment Billing: Method used to invoice customer in segments, with the total amount due divided
equally.
45
Key Terms

Invoice: Bill issued by an agency for their participation in project costs or for amounts due to an agency for
goods or services.
Open Items: Amounts billed to a customer but not paid, also known as Pending Items.
Pending Items: Receivables that have not yet been posted to an account in Cardinal.
Pro Forma: Preview of a Billing Invoice, with the option to print and view invoices before finalizing the bill.
Receivables: Amounts owed to the Department from individuals or other entities (including state, federal,
and local governments, individuals, or businesses).
Recurring Billing: Method used to reproduce bills or portions of bills on a set schedule, and generate
invoices by using templates.
46
Key Terms (continued)

The following is a list of file extensions that are allowed on attachments uploaded to Cardinal. You should
only attach key supporting documents that either enhance the electronic Cardinal transaction approval
process or are instrumental as part of the transaction history. The Cardinal system should not be relied upon
to maintain agency documentation and should not be considered the official retention source of the agency.
Supporting documents, as required by all applicable regulatory/governing bodies, should be maintained by
the agency apart from the Cardinal attachment functionality.
47
Allowed Extensions on Attachments in Cardinal
.BMP .CSV .DOC
.DOCX .JPE .JPEG
.JPG .MSG .PDF
.PNG .PST .RTF
.TIF .TIFF .TXT
.XLS .XLSX .XML
Allowed Extensions on Attachments in
Cardinal

Flowchart Key
48

